File Access Methods
File access mechanism refers to the manner in which the records of a file may be accessed. There are several ways to access files −
- Sequential access
- Direct/Random access
- Indexed sequential access
Sequential Access
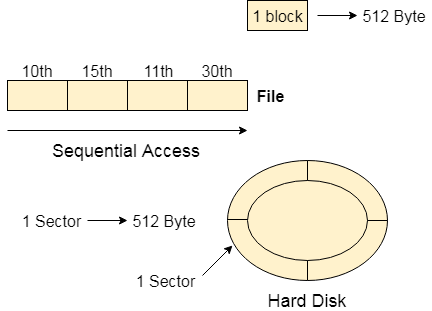
Most of the operating systems access the file sequentially. In other words, we can say that most of the files need to be accessed sequentially by the operating system.
A sequential access is that in which the records are accessed in some sequence, i.e., the information in the file is processed in order, one record after the other. This access method is the most primitive one. Example: Compilers usually access files in this fashion.
In sequential access, the OS read the file word by word. A pointer is maintained which initially points to the base address of the file. If the user wants to read first word of the file then the pointer provides that word to the user and increases its value by 1 word. This process continues till the end of the file.
Modern word systems do provide the concept of direct access and indexed access but the most used method is sequential access due to the fact that most of the files such as text files, audio files, video files, etc need to be sequentially accessed.
Direct Access
The Direct Access is mostly required in the case of database systems. In most of the cases, we need filtered information from the database. The sequential access can be very slow and inefficient in such cases.
Suppose every block of the storage stores 4 records and we know that the record we needed is stored in 10th block. In that case, the sequential access will not be implemented because it will traverse all the blocks in order to access the needed record.
Direct access will give the required result despite of the fact that the operating system has to perform some complex tasks such as determining the desired block number. However, that is generally implemented in database applications.
Random access file organization provides, accessing the records directly.
Each record has its own address on the file with by the help of which it can be directly accessed for reading or writing.
The records need not be in any sequence within the file and they need not be in adjacent locations on the storage medium.
Indexed Access
If a file can be sorted on any of the filed then an index can be assigned to a group of certain records. However, A particular record can be accessed by its index. The index is nothing but the address of a record in the file.
- This mechanism is built up on base of sequential access.
- An index is created for each file which contains pointers to various blocks.
- Index is searched sequentially and its pointer is used to access the file directly.
In index accessing, searching in a large database became very quick and easy but we need to have some extra space in the memory to store the index value.
Space Allocation
Files are allocated disk spaces by operating system. Operating systems deploy following three main ways to allocate disk space to files.
- Contiguous Allocation
- Linked Allocation
- Indexed Allocation
Contiguous Allocation
- Each file occupies a contiguous address space on disk.
- Assigned disk address is in linear order.
- Easy to implement.
- External fragmentation is a major issue with this type of allocation technique.
Linked Allocation
- Each file carries a list of links to disk blocks.
- Directory contains link / pointer to first block of a file.
- No external fragmentation
- Effectively used in sequential access file.
- Inefficient in case of direct access file.
Indexed Allocation
- Provides solutions to problems of contiguous and linked allocation.
- A index block is created having all pointers to files.
- Each file has its own index block which stores the addresses of disk space occupied by the file.
- Directory contains the addresses of index blocks of files.